Suppliers
Add your companyPowerful Edge Video Processing - Essential functionality for a wide range of ISR applications
If you design, build or supply Visual Drone Detection, create a profile to showcase your capabilities on this page.
Overview
Visual drone detection methods are widely deployed at military airbases and airfields, as well as at forward operating sites and other buildings and facilities. They are critical for management of airspaces in which UAS (unmanned aerial systems) may come into close proximity with manned aircraft, as well as for counter-UAS protection against rogue drone threats.
Visual Drone Detection
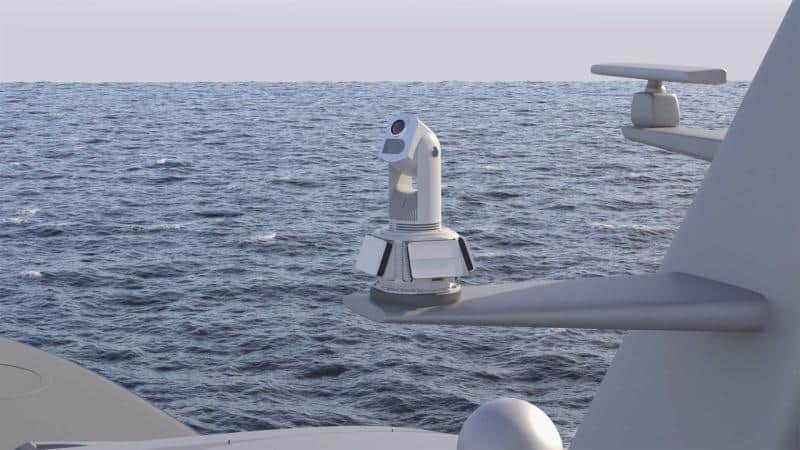
Visual drone detection systems utilize high-resolution optical cameras to scan the surrounding area and capture detailed video footage that can be analyzed for the presence of drones. These cameras are often mounted on PTZ (pan-tilt-zoom) systems that allow them to be rotated and tilted, providing coverage at angles up to 360 degrees.
In addition to fixed-site installations, drone detection systems can be provided in a range of other form factors, including portable and vehicle- or trailer-mounted. Some models allow networking of multiple cameras to provide extended coverage over wide areas.
Drone Detection Camera Systems & AI
While the footage from drone detection cameras can be monitored manually by a human, software is often used to detect potential threats in real-time, resulting in greater efficiency and reduced operator fatigue. This software may use artificial intelligence and machine learning to effectively analyze video streams, and may be trained on large datasets of drone images. This allows the software to classify threats, identify specific drone models, and reject false alarms such as birds.
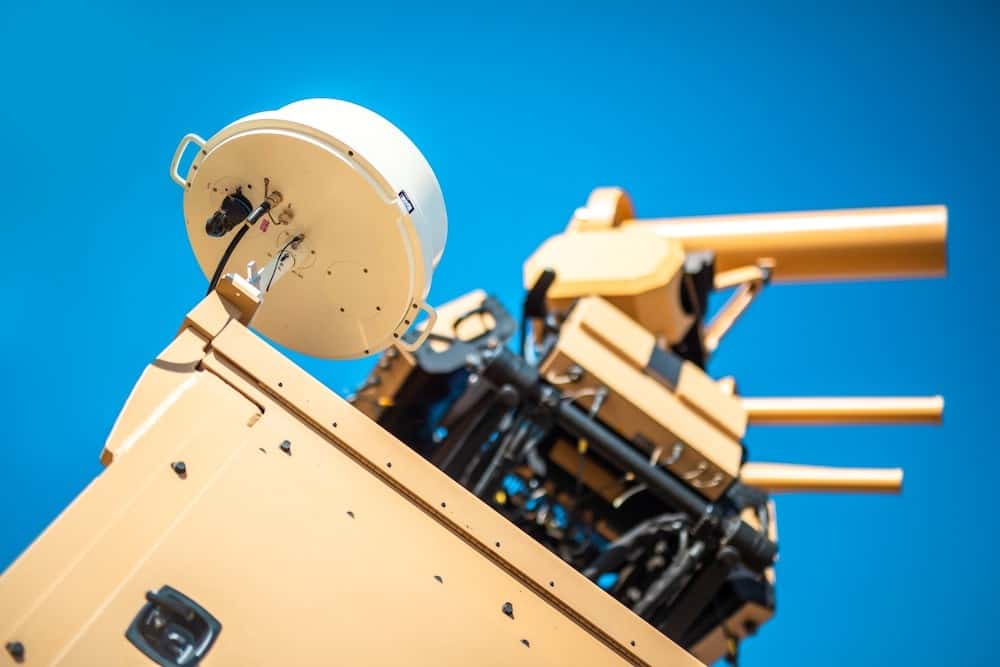
Counter UAS Systems
Visual Drone Detection Advantages
Visual drone detection allows counter-UAS systems to pick up details that other technologies may miss, such as the type of payload carried by the aircraft, and are often less expensive than other methods.
Disadvantages
They also suffer from a number of disadvantages. They may be affected by weather conditions such as fog, as well as low light levels. They may also find it difficult to detect drones in cluttered environments or in regions with physical obstacles such as mountains or heavy vegetation.
To mitigate these disadvantages, they may be combined with other anti-drone technologies, such as thermal imaging, radar, and acoustic and RF detection, to provide a more comprehensive and well-rounded solution.