Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) are vital to modern military operations, providing highly accurate positioning, navigation, and timing (PNT) capabilities across air, land, sea, and space-based platforms.
Testing of military GNSS equipment, such as receivers and antennas, is a critical part of developing these systems and integrating them into vehicles such as manned and unmanned aircraft, ground vehicles, naval vessels, and robotic platforms. GNSS testing ensures these platforms receive the precise PNT data needed for mission success, while also characterizing how equipment performs under varied and challenging conditions.
Ensuring Resilience Against Modern Threats with GNSS Technologies

GNSS simulator from CAST Navigation.
Military GNSS equipment must remain reliable in environments that include intentional interference such as jamming and spoofing attacks, as well as natural disruptions like atmospheric disturbances or terrain-induced signal loss. GNSS receivers and antennas are rigorously tested to validate their performance under such conditions, ensuring continuous operation during high-stakes missions. Testing scenarios include:
- Jamming Scenarios: Assessing receiver sensitivity to intentional signal interference.
- Spoofing Detection: Ensuring GNSS systems can identify and reject falsified signals.
- Environmental Challenges: Simulating multipath interference, urban canyon effects, and extreme weather conditions.
Live-Sky Testing
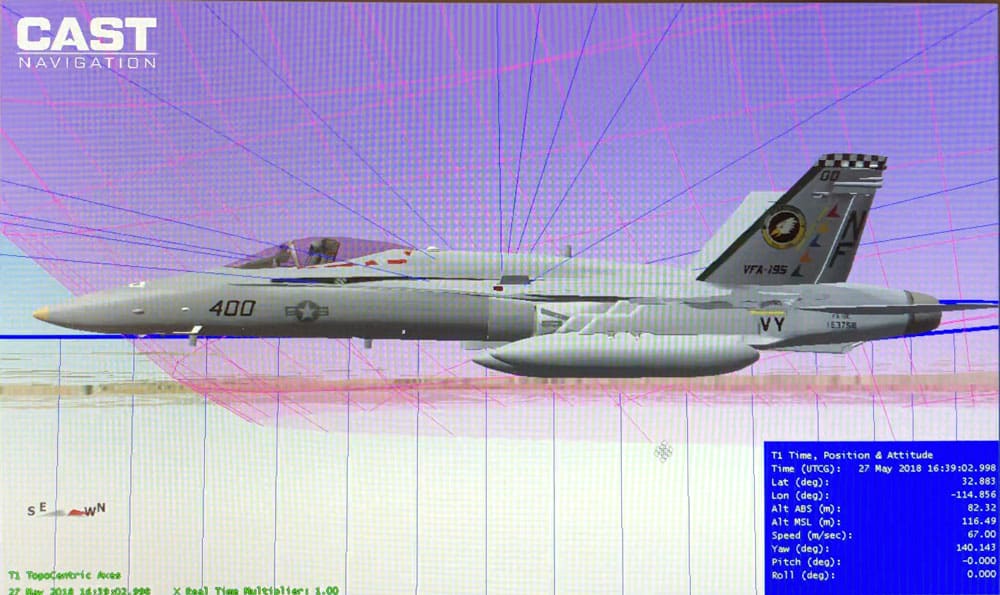
One method of testing military GNSS systems is “live-sky” testing, which involves deploying equipment in real-world field conditions. This approach provides realistic validation of laboratory and development results by exposing systems to actual satellite signals. Live-sky testing can be used to trial equipment across various geographic locations and environmental settings, helping confirm system reliability.
However, live-sky testing comes with significant drawbacks:
- Time-Consuming and Costly: Repeatedly deploying equipment on operational vehicles, such as aircraft or naval vessels, can require significant resources.
- Uncontrolled Conditions: Live-sky testing is inherently non-repeatable and subject to random errors caused by environmental variability.
As a result, live-sky testing is often supplemented or replaced by more controlled and efficient approaches.
Advanced GNSS Testing Using Signal Generators
To overcome the limitations of live-sky testing, military organizations increasingly rely on GNSS signal generators to perform robust, repeatable, and highly realistic simulations. Signal generators simulate satellite signals from all major constellations, including GPS, Galileo, BeiDou, GLONASS, SBAS, and QZSS, allowing for extensive testing in laboratory settings. These tools also enable development of systems that utilize future GNSS frequencies even before satellites are launched.
GNSS simulators provide a wide range of capabilities, including:
- Simulation of satellite positions, elevations, and orbits.
- Modeling of environmental conditions, such as atmospheric disturbances and geographic variables.
- Controlled introduction of errors, including multipath interference and antenna pattern effects.
By enabling precise replication of diverse scenarios, signal generators allow for cost-effective validation of GNSS equipment, reducing the need for extensive field testing.
GNSS Test Military Applications
Military GNSS testing supports a wide variety of defense applications, including:
Autonomous Systems
Ensuring reliable PNT data for unmanned ground vehicles, UAVs, and maritime platforms conducting reconnaissance, surveillance, and combat missions.
Precision-Guided Munitions
Validating GNSS receivers in missiles, artillery, and bombs to ensure accuracy despite electronic warfare threats.
Aviation Navigation
Testing GNSS systems for military aircraft to ensure performance during high-altitude operations, rapid maneuvers, and under signal degradation conditions.
Tactical Ground Operations
Assessing handheld and vehicle-mounted systems for reliable navigation in urban and rugged terrain environments.
Naval and Submarine Platforms
Guaranteeing navigation accuracy in open seas and under water, including the integration of GNSS with inertial navigation systems (INS).
The Role of Simulation in GNSS Development
GNSS testing solutions empower defense organizations to develop and deploy PNT systems that meet stringent operational requirements. These solutions enable engineers to create highly customized test environments, modeling specific conditions, potential threats, and performance criteria. This ensures that GNSS systems are battle-ready and capable of maintaining operational superiority across contested and GPS-denied environments.
By combining live-sky testing with advanced simulation technologies, military forces can ensure the accuracy, reliability, and resilience of GNSS systems, meeting the demands of modern defense operations.