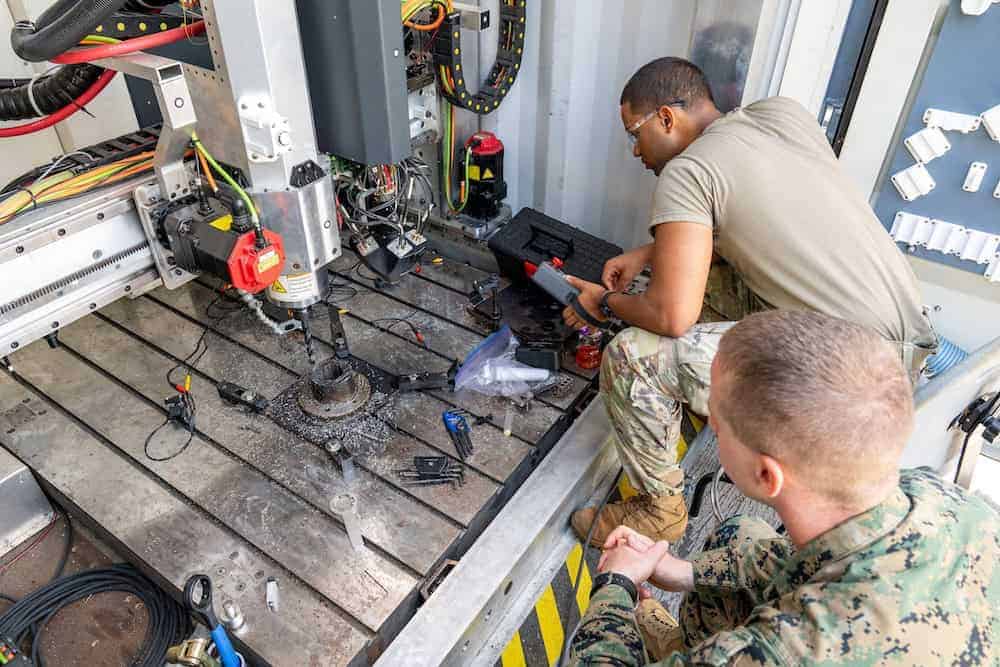
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has emerged as a game-changing technology in defense and aerospace. It enables the production of highly complex and customized components with greater efficiency, reduced material waste, and enhanced design flexibility.
Unlike traditional subtractive manufacturing methods, additive manufacturing builds parts layer by layer, allowing for intricate geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with conventional techniques.
As military and aerospace organizations seek advanced manufacturing solutions, 3D printing is increasingly being adopted for rapid prototyping, spare parts production, and the creation of mission-critical components. This technology supports defense innovation, offering significant advantages in terms of weight reduction, cost savings, and maintenance efficiency.
Table of contents:
Applications of 3D Printing in Defense Engineering
The versatility of 3D printing makes it invaluable for a wide range of defense and aerospace applications:
Aerospace Components & Jet Engine Parts
Metal 3D printing is used to manufacture engine mounts, landing gear components, and jet engine parts with high-temperature resistance and reduced weight. This enhances aircraft performance and durability.

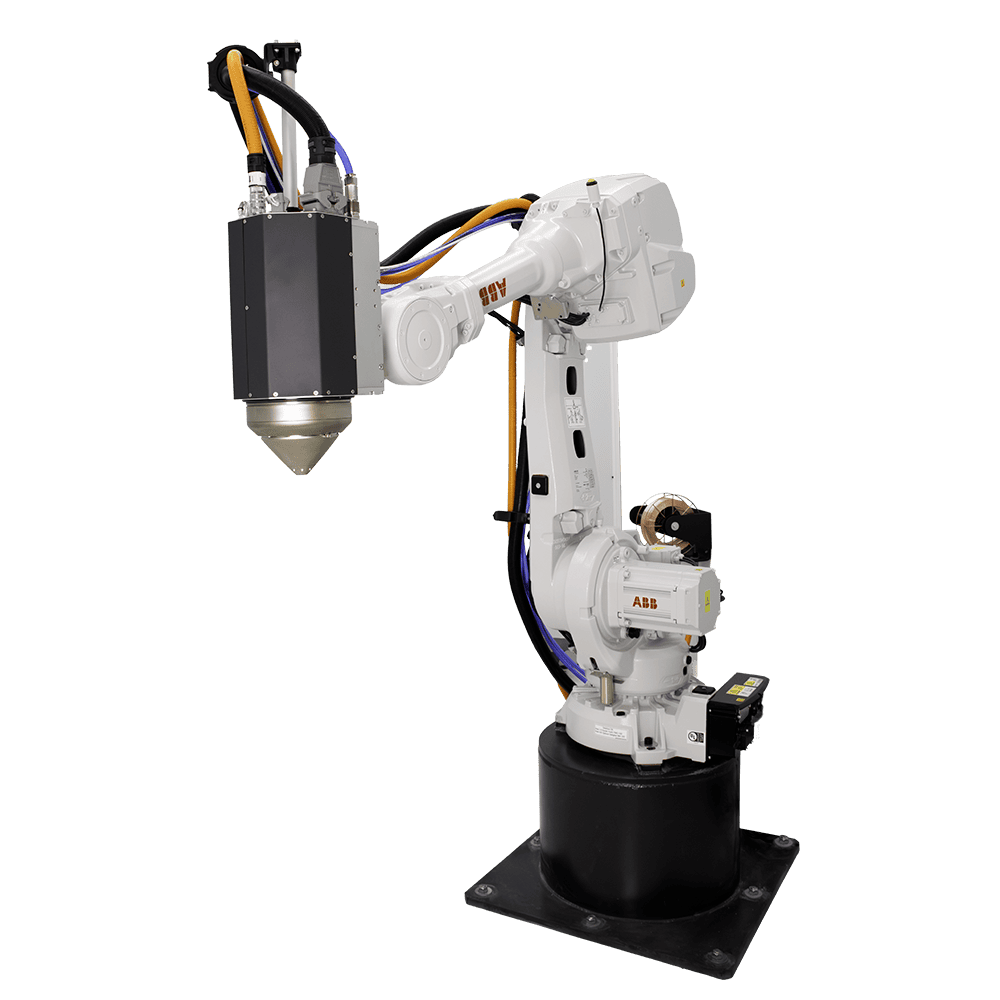
Meltio M600 3D Printer
Unmanned Systems & Drone Parts
Additive manufacturing supports the rapid production of military drone parts, sensor housings, and lightweight structures, enabling the development of next-generation unmanned systems with improved efficiency and stealth capabilities.
Maintenance, Repair & Spare Parts Production
Military forces leverage 3D printing for in-theater repairs, reducing downtime and extending the lifespan of critical assets. Technologies like directed energy deposition and cold spray additive manufacturing are particularly useful for refurbishing damaged equipment.
Satellite Structures & Thermal Protection Systems
The space industry benefits from 3D-printed satellite structures, which offer improved strength-to-weight ratios and can withstand extreme thermal conditions. Metal and composite additive manufacturing contribute to advanced thermal protection systems.
Stealth Technology & Defense Innovation
Defense contractors use 3D printing to develop stealth technology, including radar-absorbing structures and low-signature components for next-generation military platforms. This enhances survivability and operational effectiveness.
Types of 3D Printing Technology Used in Defense
Various 3D printing technologies are utilized in defense and aerospace, each offering unique advantages depending on the application and material requirements.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) & Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
SLS and FDM are widely used for polymer and composite 3D printing. SLS employs a laser to fuse powdered materials into solid structures, while FDM extrudes thermoplastic filaments layer by layer. These methods are ideal for lightweight drone parts, sensor housings, and rapid prototyping.
Stereolithography (SLA) & Digital Light Processing (DLP)
SLA and DLP use photopolymerization to create highly detailed components with smooth surface finishes. These processes are valuable for creating precision prototypes, custom casings, and optical components for defense electronics.
Metal Additive Manufacturing: SLM, DMLS & EBM
Metal 3D printing technologies such as selective laser melting (SLM), direct metal laser sintering (DMLS), and electron beam melting (EBM) allow for the production of high-strength aerospace components. These techniques are essential for manufacturing jet engine components, structural aircraft parts, and heat-resistant satellite structures.
Binder Jetting & Directed Energy Deposition (DED)
Binder jetting is a cost-effective approach for producing metal and ceramic parts, while DED, including cold spray additive manufacturing, enables on-demand repair and refurbishment of military equipment. These methods enhance supply chain resilience by allowing in-field part production.
Benefits of 3D Printing in Defense and Aerospace
The adoption of 3D printing in defense engineering offers several strategic benefits:
Rapid Prototyping & Design Flexibility
3D printing accelerates the development of new defense technologies by enabling engineers to quickly create and test prototypes. This reduces the time required to transition from concept to deployment.
Cost Efficiency & Material Savings
Traditional manufacturing often results in significant material waste. Additive manufacturing minimizes waste by using only the necessary material to build a part, leading to substantial cost savings over time.

Meltio Robot Cell 3D Printing Solution
Lightweight Materials & Enhanced Performance
Weight reduction is critical in aerospace applications. 3D printing allows for the creation of lightweight yet strong components, improving fuel efficiency and payload capacity in aircraft and unmanned systems.
On-Demand Production & Supply Chain Resilience
By enabling decentralized production, 3D printing reduces dependence on complex global supply chains. Military forces can produce spare parts and mission-critical components on-site, ensuring operational readiness even in remote locations.
Customization & Complex Geometries
Defense applications often require highly specialized components. 3D printing supports mass customization and the creation of intricate designs that enhance performance, such as radar components and stealth technology applications.
Advancing Defense Manufacturing with 3D Printing
3D printing is redefining defense and aerospace manufacturing by offering innovative solutions for prototyping, production, and maintenance. With its ability to create lightweight, high-performance components while reducing costs and lead times, this technology is becoming an integral part of defense engineering.
As military and aerospace organizations continue to adopt additive manufacturing, the future promises even greater advancements in mission-critical component design, supply chain resilience, and operational efficiency.